// Step 1: Build row-wise consecutive 1s
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
rowOnes[i][j] = (j == 0) ? 1 : rowOnes[i][j - 1] + 1;
}
}
}
// Step 2: For each cell, go upwards and find minimum width to count rectangles
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
int minWidth = rowOnes[i][j];
for (int k = i; k >= 0 && rowOnes[k][j] > 0; k--) {
minWidth = Math.min(minWidth, rowOnes[k][j]);
count += minWidth;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
Pattern: Moving in four cardinal directions (up, down, left, right) or diagonally across a matrix
Common Problems:
Best Approach:
Use a directions array to simplify movement across the grid.
DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}} // right, down, left, up
For diagonal moves:
DIAGONAL_DIRECTIONS = {{1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}}
Implement BFS or DFS to visit neighboring cells.
Examples:
You are given an image represented by an m x n grid of integers image, where image[i][j] represents the pixel value of the image. You are also given three integers sr, sc, and color. Your task is to perform a flood fill on the image starting from the pixel image[sr][sc].

**Input:**
image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]], sr = 1, sc = 1, color = 2
Output:
[[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation**:**
From the center of the image with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1) (i.e., the red pixel), all pixels connected by a path of the same color as the starting pixel (i.e., the blue pixels) are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not horizontally or vertically connected to the starting pixel.
class Solution {
// Directions: right, down, left, up
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1},
{-1, 0}};
// O(1)
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int originalColor = image[sr][sc];
// If the original color is the same as the new color, no need to proceed
if (originalColor != newColor) {
dfs(image, sr, sc, newColor, originalColor);
}
return image;
}
private void dfs(int[][] image, int i, int j, int newColor,
int originalColor) {
if (i < 0 || i >= image.length || j < 0 || j >= image[0].length
|| image[i][j] != originalColor) {
return;
}
image[i][j] = newColor;
for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) {
int newRow = i + direction[0];
int newCol = j + direction[1];
dfs(image, newRow, newCol, newColor, originalColor);
}
}
}
N is the total number of pixels in the image. Every pixel is visited once.N in the worst case (when all pixels are connected).Dry Run:
(i, j) is (1, 1)
image[1, 1] = 2
(i, j) is (1, 0)
image[1, 0] = 2
(i, j) is (2, 0)
image[2, 0] = 2
(i, j) is (1, 0) ⇒ 2 ≠ 1 ⇒ Recursive Check 10image[0, 0] = 2
(i, j) is (0, 0)
image[0, 0] = 2
(i, j) is (0, 1)
image[0, 2] = 2
+11 calls where validation fails ( +3 for (0, 2), +4 for (2, 1) and +4 for (2, 2) )Therefore, the following are the vertices where we modified the pixel color:
( 1 , 1 )
( 1 , 0 )
( 2 , 0 )
( 0 , 0 )
( 0 , 1 )
( 0 , 2 ) ⇒ 6 calls
Total number of recursive calls: 25 (14 + 11)
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of '1's (land) and '0's (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
Example 1:
Input:
grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input:
grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
Output: 3
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j] is '0' or '1'.class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int numIslands = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
numIslands++;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return numIslands;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || grid[i][j] != '1') {
return;
}
grid[i][j] = '0';
for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) {
int newRow = i + direction[0];
int newCol = j + direction[1];
dfs(grid, newRow, newCol);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
char[][] grid = {
{'1', '1', '1', '1', '0'},
{'1', '1', '0', '1', '0'},
{'1', '1', '0', '0', '0'},
{'0', '0', '0', '0', '0'}
};
int result = solution.numIslands(grid);
System.out.println("Number of Islands: " + result); // Output: 1
}
}
Thus, the time complexity ****is O(m × n) and the space complexity ****is also O(m×n) where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns in the grid.
package com.sai.designPatterns;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public static void rotateByOneCell(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return;
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
int[] temp = new int[2 * (m + n - 2)];
int index = 0;
// Top row (left to right)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
temp[index++] = matrix[0][j];
}
// Right column (top to bottom)
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
temp[index++] = matrix[i][n - 1];
}
// Bottom row (right to left)
for (int j = n - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
temp[index++] = matrix[m - 1][j];
}
// Left column (bottom to top)
for (int i = m - 2; i > 0; i--) {
temp[index++] = matrix[i][0];
}
// [1, 2, 3, 10, 10, 11, 9, 8, 7, 4]
int lastValue = temp[temp.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, temp, 1, temp.length - 1);
// [1, 1, 2, 3, 10, 10, 11, 9, 8, 7]
temp[0] = lastValue;
index = 0;
// [4, 1, 2, 3, 10, 10, 11, 9, 8, 7]
// Top row (left to right)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[0][j] = temp[index++];
}
// Right column (top to bottom)
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
matrix[i][n - 1] = temp[index++];
}
// Bottom row (right to left)
for (int j = n - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
matrix[m - 1][j] = temp[index++];
}
// Left column (bottom to top)
for (int i = m - 2; i > 0; i--) {
matrix[i][0] = temp[index++];
}
System.out.println("\\nRotated Matrix by one cell clockwise:");
for (int[] row : matrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 3, 10},
{4, 5, 6, 10},
{7, 8, 9, 11}
};
System.out.println("Original Matrix:");
for (int[] row : matrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
rotateByOneCell(matrix);
}
}
package com.sai.designPatterns;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution1 {
public static void rotateByOneCellAnticlockwise(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return;
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
// Temporary array to store the outer ring values
int[] temp = new int[2 * (m + n - 2)];
int index = 0;
// Top row (left to right)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
temp[index++] = matrix[0][j];
}
// Right column (top to bottom)
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
temp[index++] = matrix[i][n - 1];
}
// Bottom row (right to left)
for (int j = n - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
temp[index++] = matrix[m - 1][j];
}
// Left column (bottom to top)
for (int i = m - 2; i > 0; i--) {
temp[index++] = matrix[i][0];
}
// Store the first value to rotate anticlockwise
int firstValue = temp[0];
System.arraycopy(temp, 1, temp, 0, temp.length - 1);
temp[temp.length - 1] = firstValue;
index = 0;
// Top row (left to right)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[0][j] = temp[index++];
}
// Right column (top to bottom)
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
matrix[i][n - 1] = temp[index++];
}
// Bottom row (right to left)
for (int j = n - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
matrix[m - 1][j] = temp[index++];
}
// Left column (bottom to top)
for (int i = m - 2; i > 0; i--) {
matrix[i][0] = temp[index++];
}
System.out.println("\\nRotated Matrix by one cell anticlockwise:");
for (int[] row : matrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 3, 10},
{4, 5, 6, 10},
{7, 8, 9, 11}
};
System.out.println("Original Matrix:");
for (int[] row : matrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
rotateByOneCellAnticlockwise(matrix);
}
}
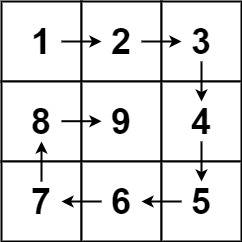
Given a positive integer n, generate an n x n matrix filled with elements from 1 to n2 in spiral order.
Example 1:

Input: n = 3
Output: [[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 20